NIST Framework is a good base to create a security policy.
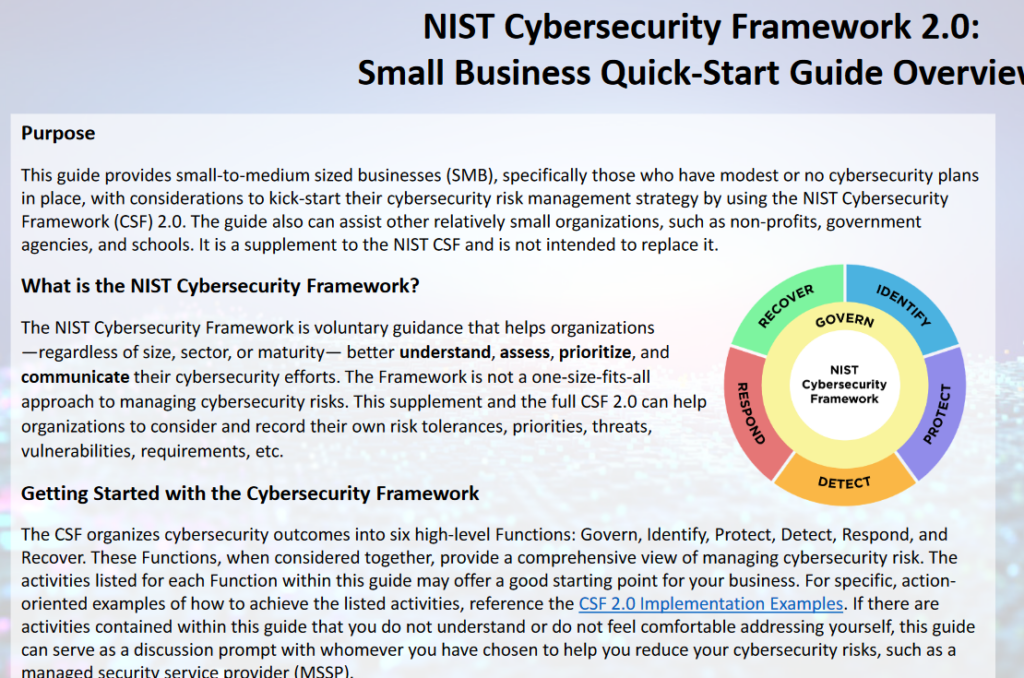
I have discussed NIST Framework at my blogsite (oversitesentry.com) and there are 6 pieces to the framework:
- Govern
- Identify
- Protect
- Detect
- Respond
- Recover
I have also discuss NIST framework on the latest post on October 2024
Then we have PCI compliance with 12 sections to keep in mind and guide us on the path to making a security policy.
I have an older page that is still relevant – PCI compliance can be a good start to a security policy the 12 sections
- Firewall maintenance (set up proper procedures to edit the ACL – Access Control List)
- Change your default passwords (and create a password policy)
- Protect stored cardholder data (if you are not developing software or have a website that you are developing – this may not be necessary)
- Encrypt Cardholder data – i.e. use devices that encrypt cardholder data (or develop this properly)
- Protect all systems against malware (using anti-virus software)
- Develop and maintain secure applications (only if you are developing software)
- Restrict access to cardholder data (if developing authenticate before giving access)
- Identify and authenticate access to system components
- Authentication physical access (only qualified people should access credit card systems)
- Track and monitor all access to network resources and cardholder data (log systems)
- regularly test security systems and procedures
- Maintain a policy that addresses security information for all personnel
NIST and PCI standards org have created mapping documents:
These documents were made at PCI 3.2.1 (not 4.0 which is current today). But there were not that many changes for most small businesses (cloud companies and credit card processors received the bulk of the changes).
Also if you look at all the categories in NIST Cybersecurity framework then you will see items as supply chain risk management and other controls. The focus is this paragraph from this sitezengrc.com:
NIST Frameworks: Primarily aimed at enhancing cybersecurity within U.S. critical infrastructure providers (e.g., energy, financial services), the NIST frameworks offer guidelines for creating, implementing, and managing an information security program. NIST SP 800-53 and NIST SP 800-171 specify security controls for federal agencies and their contractors to meet compliance requirements under FISMA and DFARS, respectively.
If you are one of the small businesses without a supply chain and may not deal with the federal government then you may not need the full NIST cybersecurity framework. It is good to keep in mind the 6 sections as mentioned above.
Claude gave this answer with a question – of creating a security policy using PCI compliance and NIST framework for small business:
# Small Business Cybersecurity and Data Protection Policy ## 1. Purpose and Scope ### 1.1 Objective This security policy is designed to protect the organization's information assets, ensure compliance with PCI DSS and NIST Cybersecurity Framework standards, and mitigate potential cybersecurity risks. ### 1.2 Scope This policy applies to: - All employees, contractors, and third-party vendors - All information systems, networks, and data assets - Physical and digital environments where company data is processed or stored ## 2. Governance and Risk Management ### 2.1 Security Leadership - Designate a Security Officer responsible for: - Implementing and maintaining the security program - Conducting regular risk assessments - Ensuring compliance with PCI DSS and NIST guidelines ### 2.2 Risk Assessment and Management - Conduct annual comprehensive risk assessments - Maintain a risk register documenting: - Identified risks - Potential impact - Mitigation strategies - Residual risk levels ## 3. Access Control ### 3.1 User Access Management - Implement principle of least privilege - Maintain formal user access authorization process - Require multi-factor authentication for: - Administrative accounts - Remote access - Sensitive systems ### 3.2 Authentication Controls - Enforce strong password policies: - Minimum 12 characters - Complex password requirements - Mandatory 90-day password rotation - Account lockout after 5 failed attempts ### 3.3 Third-Party Access - Develop vendor access management protocol - Require vendor security assessments - Implement time-limited and monitored access for external parties ## 4. Network and System Security ### 4.1 Network Protection - Implement and maintain: - Firewalls - Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) - Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) - Segment network to isolate sensitive systems - Regularly update and patch network infrastructure ### 4.2 Endpoint Protection - Deploy and maintain endpoint protection on all devices: - Antivirus/Antimalware software - Host-based firewalls - Regular vulnerability scanning ### 4.3 Data Encryption - Encrypt data at rest and in transit - Use industry-standard encryption protocols (TLS 1.2+) - Secure key management processes ## 5. Incident Response and Business Continuity ### 5.1 Incident Response Plan - Develop and maintain a comprehensive incident response plan - Define clear roles and responsibilities - Establish communication protocols - Conduct annual tabletop exercises ### 5.2 Incident Detection and Reporting - Implement 24/7 security monitoring - Establish incident reporting mechanisms - Create incident severity classification system ### 5.3 Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery - Develop and test annual disaster recovery plan - Maintain offsite and encrypted data backups - Establish recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPO) ## 6. Data Protection and Privacy ### 6.1 Data Classification - Classify data based on sensitivity: - Public - Internal - Confidential - Restricted ### 6.2 Payment Card Handling - Strict compliance with PCI DSS requirements - Minimize and protect cardholder data - Use tokenization and truncation techniques - Prohibit storage of sensitive authentication data ## 7. Employee Training and Awareness ### 7.1 Security Awareness Program - Mandatory annual security awareness training - Quarterly phishing simulation exercises - Regular updates on emerging threats - Role-specific security training ### 7.2 Acceptable Use Policy - Define acceptable use of company resources - Outline consequences of policy violations - Address personal device usage ## 8. Compliance and Audit ### 8.1 Regulatory Compliance - Annual PCI DSS compliance assessment - Quarterly internal security audits - Maintain documentation for all security controls ### 8.2 Continuous Improvement - Regular policy review and update - Incorporate lessons learned from incidents - Stay informed about emerging cybersecurity standards ## 9. Physical Security ### 9.1 Facility Access Control - Implement access control systems - Maintain visitor logs - Secure server rooms and critical infrastructure - Use security cameras and access monitoring ## 10. Policy Enforcement ### 10.1 Disciplinary Procedures - Clear consequences for security policy violations - Progressive disciplinary actions - Potential termination for serious breaches ## Appendices - Incident Response Workflow - Risk Assessment Template - Security Control Inventory - Vendor Security Assessment Checklist ## Policy Revision History - Initial Version: [Date] - Last Reviewed: [Date] - Next Review Date: [Date]
This is a basic way I create a security policy – then I will go back and forth with customer and information technology person. Yes one of the first things to do is to get the security policy “point person”. The customer business must have someone who is in charge of the security program.